Traceability systems for the food industry
At SIVART we have developed and installed the traceability software SiTraza unit, adapting it according to the sector, connecting and integrating the new technologies of marking, reading, connection to PLC’s, MES / SCADA systems and artificial vision.
Some of the sectors that use our traceability traceability software are:
- Pharmaceutical Sector
- Automotive
- Cosmetics and Perfumery
- Alimentaria
- General Industry
Food traceability control is a particularly serious issue, since people’s health can sometimes be affected by food in poor condition or that does not comply with any requirement that makes it unsuitable for sale to the public.
In order to eradicate any incidence of this type, traceability of food products is necessary.
Contact us for more information for more information related to the food traceability systems that Sivart offers.
Food traceability regulations
In view of the seriousness of food traceability, the AESAN, the AESAN (Spanish Agency for Food Safety and Nutrition) is contemplating a regulations that details all the points that companies working in the world of food must comply with.
On the one hand, in the event of any irregularity, thanks to food safety traceability, it is possible to identify all the points through which the product has passed.
The affected companies must comply with the following:
- Recall products that do not conform to safety requirements
- Provide relevant information for traceability.
- Cooperate with producers, processors, manufacturers and authorities.
On the other hand, they must inform the competent authorities if they consider or have reason to believe that any of the products they market do not comply with safety regulations.
According to European Union rules and regulations, the food traceability system must comply with:
- Participants in the supply chain:
This includes farmers, producers, transporters and distributors.
- The State:
He is in charge of ensuring compliance with the regulations and in case of incidents to ensure that each participant fulfills his role and obligations.
- The European Union:
The European Union is responsible for issuing EU legislation to be applied by all member states. It also regulates quality and safety standards and coordinates actions between the authorities of the different member states where appropriate.
Food identification codes
Two methods of identification are widely used: barcodes and RFID technology.
- Barcodes: This is one of the most widely used techniques at present. It is characterized for being a labeling that has the product with a bar code that must comply with global food traceability guidelines.
- RFID technology: This is a wireless communication system. And when compared to the bar code, instead of having ink it simply uses radio waves. This system has grown a lot in recent times also due to technological advances in the sector.
The identifying elements must contain the following information:
- Lot number
- From whom and what products are received
- Shelf life, processing and packaging dates
- Ingredients, conditions of use and storage.
- Product status
- A way to contact the supplier in case of problems.
What is food traceability?
Food traceability is simply a very important quality management method. It is a guarantee that food arrives in good condition to the final consumer. Traceability makes it possible to trace the entire path that a food has taken from its origin to the end, so that in the event of any risk (mainly health risks), it can be detected and acted upon as quickly as possible.
The stages of food traceability are as follows:
- Production Phase
- Transformation phase
- Distribution phase
Types of food traceability
Currently, we are aware of 3 types of food traceability.
- Forward traceability
This type of traceability is common in wholesalers or large food industries. It consists of applying an extra level (the 3rd) called forward traceability and involves rigorously recording the sale of processed products (company data, batch number, quantities sold of each batch…).
- Internal food traceability
It refers to the moment when the products are divided, changed or mixed, what is produced, from what, how, when and, finally, the final identification of the product.
- Backward traceability
It consists of requiring suppliers to use all the required documentation on the premises to ensure traceability up to the moment. That is to say, to continue the chain
At Sivart, we are aware that tracking or traceability systems are complicated, that is why with our equipment we guarantee good results that ensure the veracity of this system. If it is not done correctly, any product or company could be in danger (if any food reaches your hands in bad conditions).
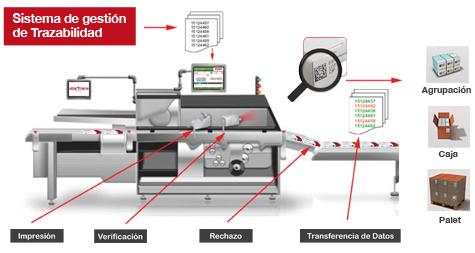
Example of food product traceability
To complement the article we have dedicated to food traceability, we would like to end with an example of food product traceability from the document: “Food traceability in the food industry”.Traceability. Importance and key data to control. Practical examples “of the Subdirección General de Medios de Producción Ganaderos MAPA (MAPA’s General Subdirectorate of Livestock Production Means). We hope you find it useful.
If you have any doubts about traceability systems in the food sector that exist. Contact us without obligation, our specialists will advise you and offer you different solutions adapted to your project.